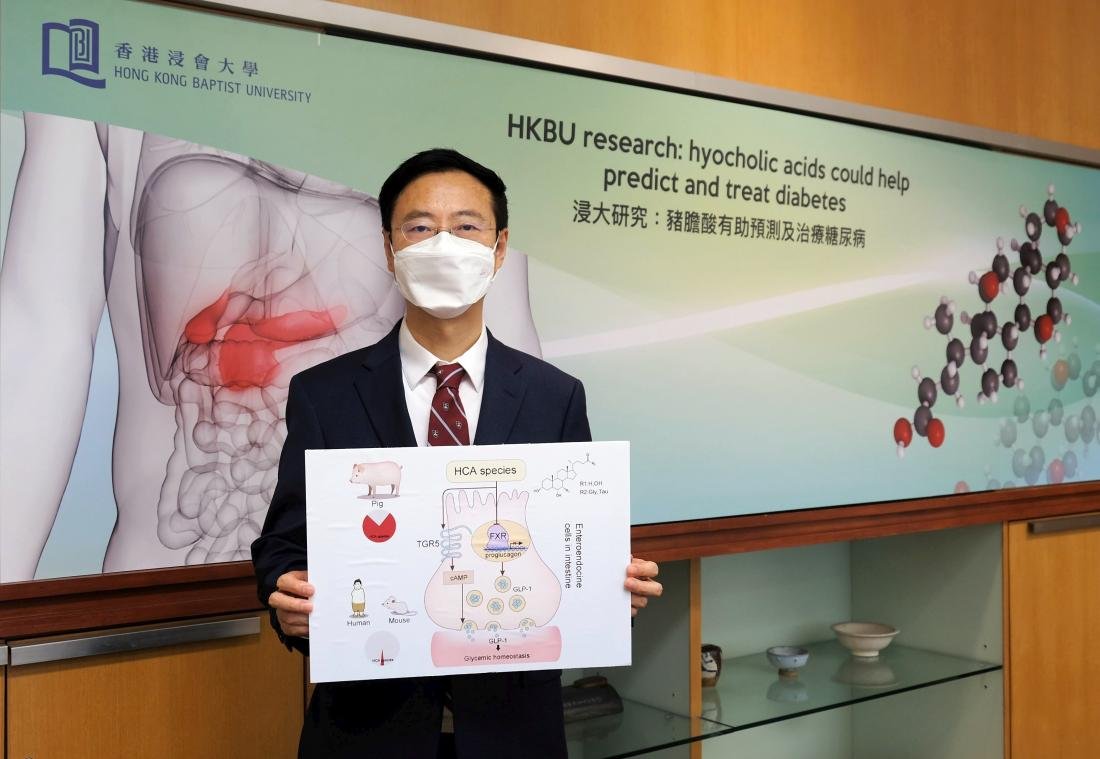
Photo Credit: Hong Kong Baptist University (HKBU)
A series of studies led by researchers from Hong Kong Baptist University (HKBU) have revealed that hyocholic acid and its derivatives (collectively known as HCAs), a component of bile acids that facilitate fat digestion, are a promising risk indicator of type 2 diabetes.
The strong efficacy of HCAs in regulating blood glucose levels and protecting against diabetes has also been uncovered. The findings open a window for the development of HCA-based predictive markers as well as anti-diabetic drugs.
The research results have been published in the international scientific journals Cell Metabolism and Nature Communications.
HCAs play a major role in regulating blood glucose levels. HCAs constitute nearly 2% of bile acids in humans scientists observed a negative correlation between HCAs and blood glucose levels. The study indicates the potential role of HCAs in the maintenance of stable glucose levels. It was discovered that the levels of serum HCAs were significantly lower in the healthy obese and obese with type 2 diabetes groups. Those who had become metabolically unhealthy had significantly lower baseline levels of serum HCAs, illustrating that levels of HCAs are a strong predictor of metabolic syndromes such as diabetes. The study also revealed that HCAs are the most effective at stimulating GLP-1 secretion when compared with other types of bile acids. The findings disclosed that HCAs regulate blood glucose levels by stimulating the secretion of GLP-1 and thus insulin production.
Potential for diabetes prediction and treatment
“The results of our studies provide evidence of how HCAs help to regulate blood glucose levels, and they have revealed the mechanism of how it is achieved at a cellular level. HCAs demonstrate promising potential, and they could be developed into an agent for the prediction and treatment of type 2 diabetes. As gut microbiota can regulate the metabolism of HCAs, targeting the intestines instead of the pancreas could be a prospective novel strategy for treating diabetes. We will further investigate how to increase the secretion levels of HCAs in diabetic patients by regulating the intestinal bacteria” said Professor Jia.
Image Caption: Professor Jia Wei, Chair Professor of the School of Chinese Medicine at HKBU, has revealed that hyocholic acid and its derivatives are a promising risk indicator of type 2 diabetes.