image credit- shutterstock
Viridian Therapeutics, Inc., a US-based biopharmaceutical company focused on discovering, developing, and commercialising potential best-in-class medicines for serious and rare diseases, has entered into an exclusive collaboration and license agreement with Kissei Pharmaceutical Co. to develop and commercialise veligrotug and VRDN-003 in Japan.
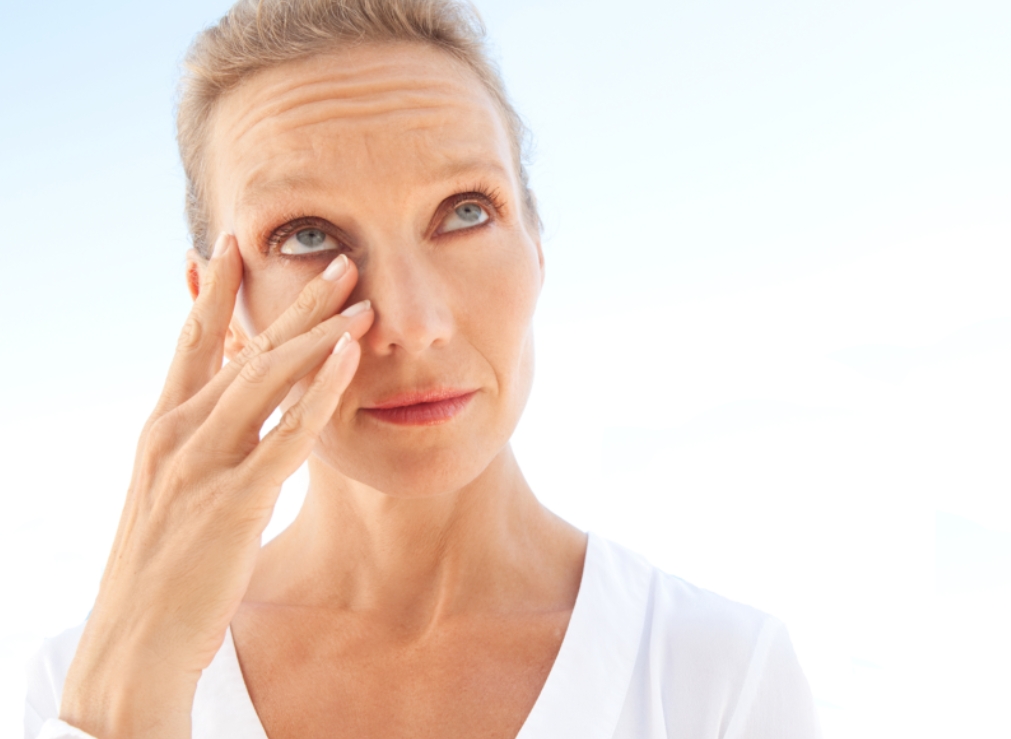
Both molecules are anti-insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF-1R) antibodies for the potential treatment of patients with thyroid eye disease (TED), and VRDN-003 is a potential best-in-class, subcutaneous, half-life extended anti-IGF-1R antibody with the same binding domain as veligrotug. TED is an autoimmune condition characterised by inflammation, growth, and damage to tissues around and behind the eye, often causing swelling, discomfort, and double vision, among other signs and symptoms.
Under the terms of the agreement, Viridian will grant Kissei an exclusive license to develop and commercialize veligrotug and VRDN-003 in Japan. Viridian will receive an upfront cash payment of $70 million, with the potential to receive an additional $315 million in development, regulatory, and commercial milestone payments, as well as tiered royalties on net sales in Japan with percentages ranging from the 20s to mid-30s. Kissei will be responsible for all development, regulatory, and commercialization activities, and associated costs, in Japan.